Rasmussen and Lind: Coping With Complexity
Tags: papers, complexity
Talks about how people cope with complexity in power plants
Decision models:
- Take some data, integrate the data, evaluate and make a decision, and coordinate the acts with an intention in mind
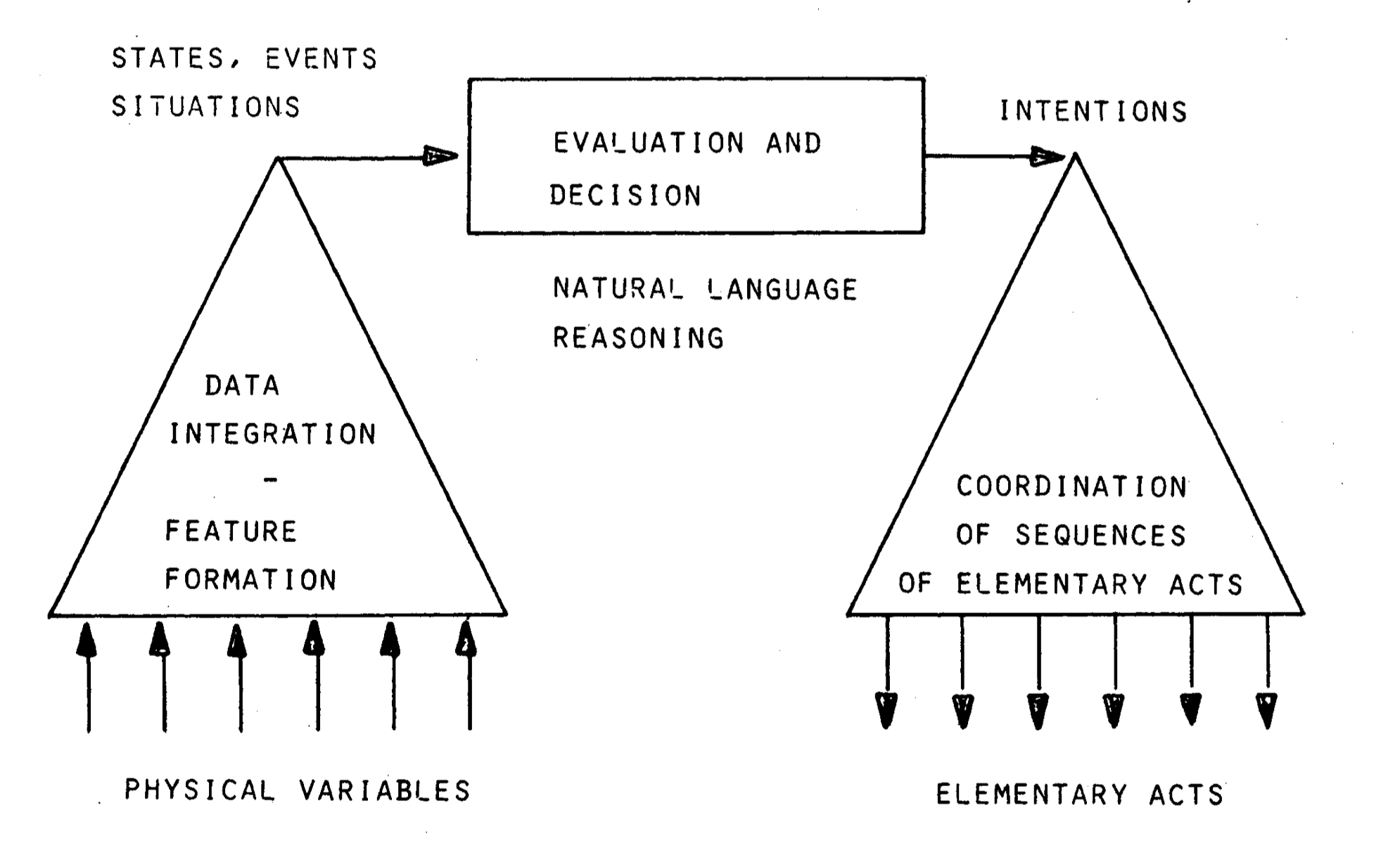
Simple heuristics taken:
- Thresholds - when a variable crosses an absolute threshold
- Like a threshold in grafana - “IO wait in CPU usage occupying more than 50%, I know that the CPU is spending time waiting on IO, resolution is involved with IO”
- Deviation from normal - when an experienced operator knows what is normal and what is not
- Deviation from normal - “current time is outside of p99”
Abstraction Hierarchies
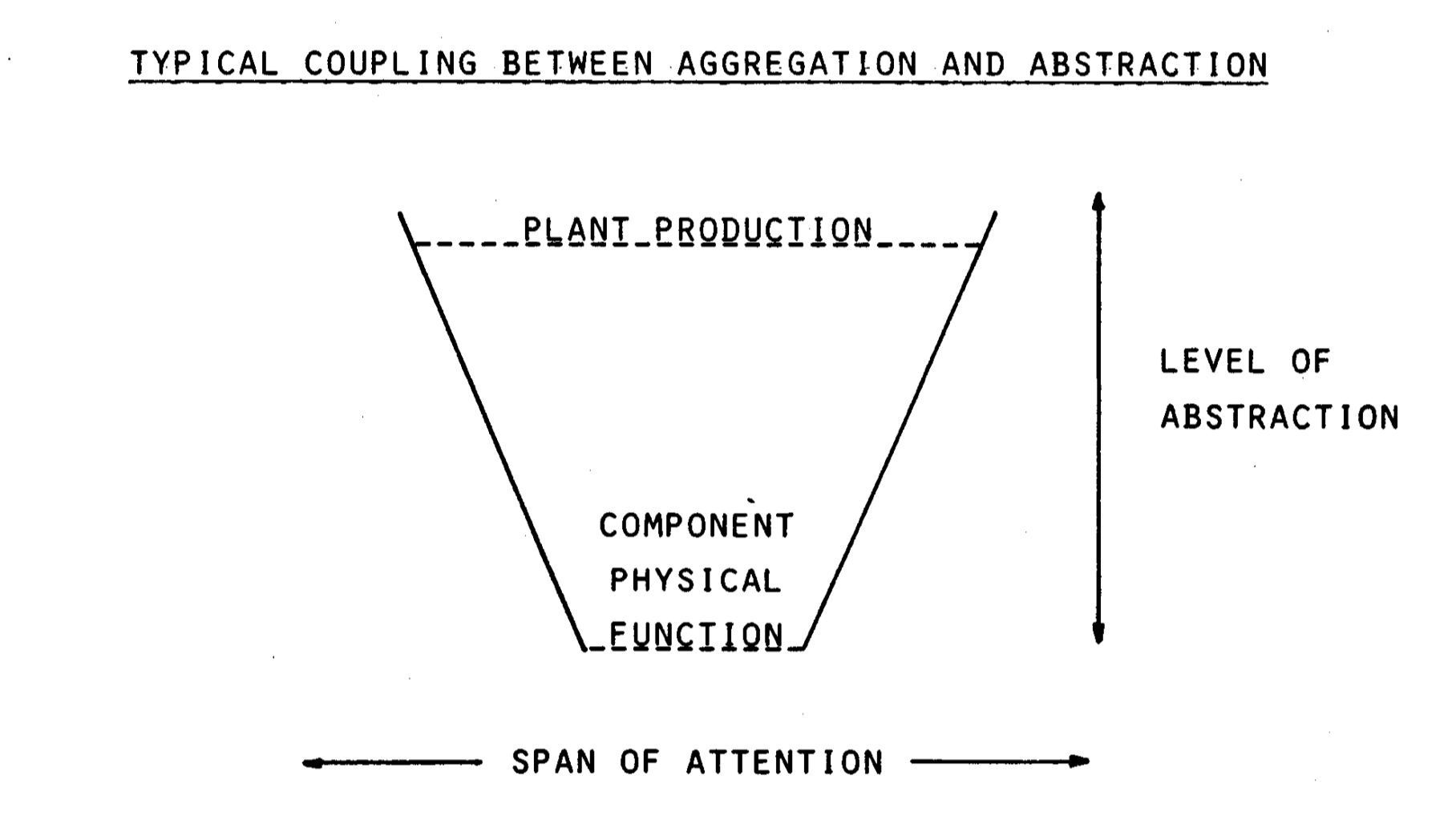
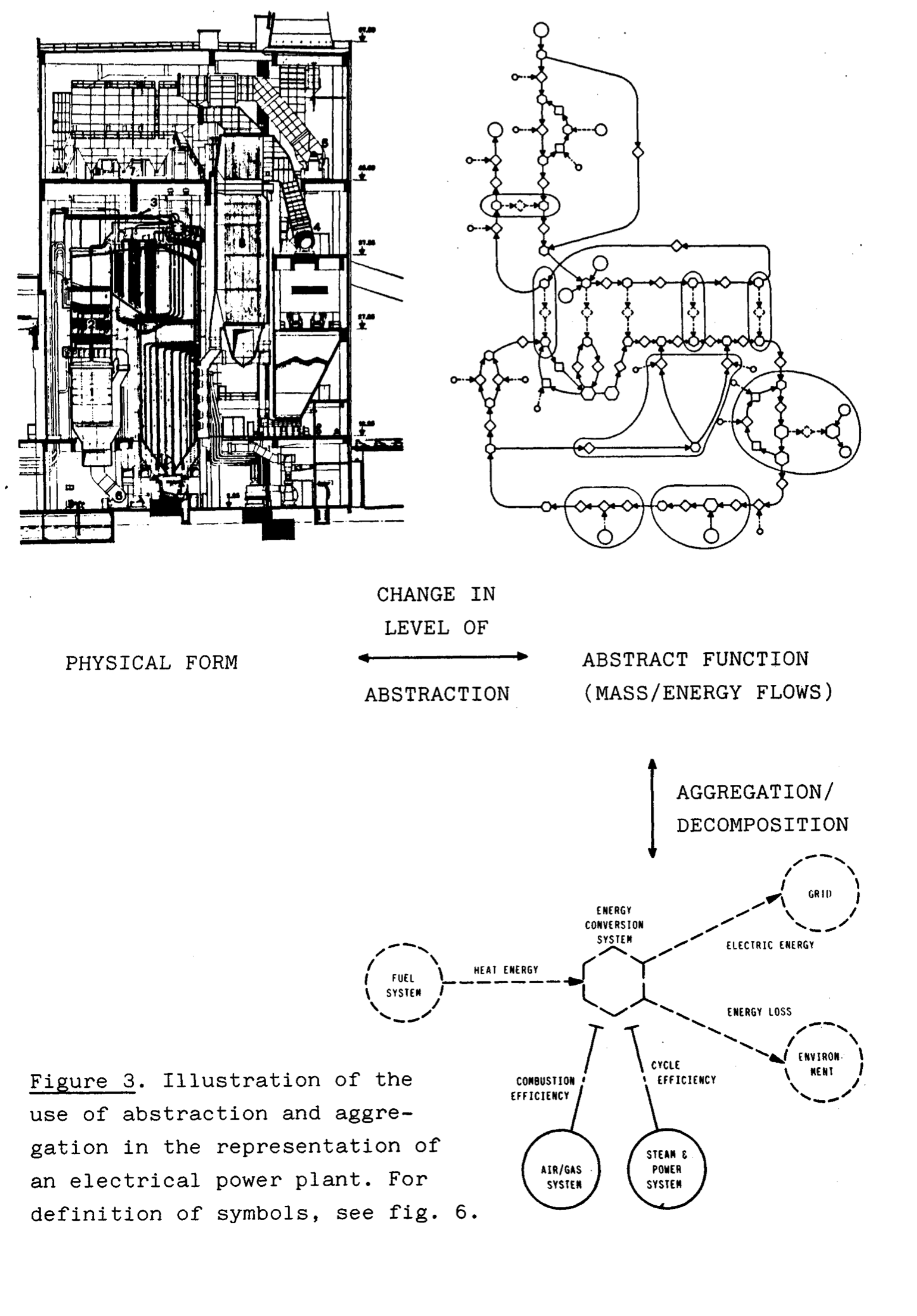 Physical form relates to the abstract function, which relates to the general understanding
Physical form relates to the abstract function, which relates to the general understanding
- Information is not necessarily removed removed, information at higher levels is added based on higher level principals. We “remove” infomration by asserting that there is some set of assumptions now on the lower level.
- A struct is an abstraction over raw groups, it asserts that the memory will be laid out in a specific manner, that the members of the struct behave a certain way, etc
Important to establkish a number of autonomous functional units at one level before they can be connected to one functional unit at the next level
Each level of abstraction has the reasons and specifications coming from below, therefore abstractions are built from bottom-up but viewed top-down. In the case of disturbances due to technical faults, the causes of malfunction are propagating bottom-up through the hierarchy of abstraction, at the same time as rules for peroper functions are derived top-down.