cpu
Tags: computers
TLBs
- In normal multiprocessors, each CPU has it’s own TLB, usually some split of small entries and big entries
SPARC
Registers
- Nowadays, all registers can be used as general purpose registers
- RBP is used as a general purpose one, with RSP taking the role as a frame pointer. RIP is still in the stack memory region for each function call
info registersin gdb- Constants are encoded in instructions, but arbitrary values are retrieved from memory
- Goto is a
JMP - Function calls are
CALL - When a function is called from a caller, the callee needs to make room for local variables. In 64bit x86, usually the first six arguments are passed in registers
- Then it saves the base pointer into RBP, and then sets up the new base ptr
Cache Lines
- https://lore.kernel.org/netdev/[email protected]/
- Aligning structs in TCP gives a ton of improvements!
Types of Caches
Direct Mapped Cache
- Like consistent hashing, each memory address is used to map a block to a specific cache line
- both provide deterministic mapping
Fully Associative Cache
- Memory can be stored in any cache line, but we need to search to find it
Set Associative
- Memory address is used to determine the set, and the data can be placed in any block within the set
Load-Linked and Store-Conditional (LL/SC)
- Pair of instructions used in concurrent programming
- Achieves syncronization without locks
- Load-Linked - reads the current value from memory location and “links” it, typically by marking the address in a special way within the processor
- Store-Conditional - attempts to write a new value to the memory location that was read by LL. Write will only succeed if the location has not been udpated since LL was executed
Skylake
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BVVNtG5dgks
- frontend
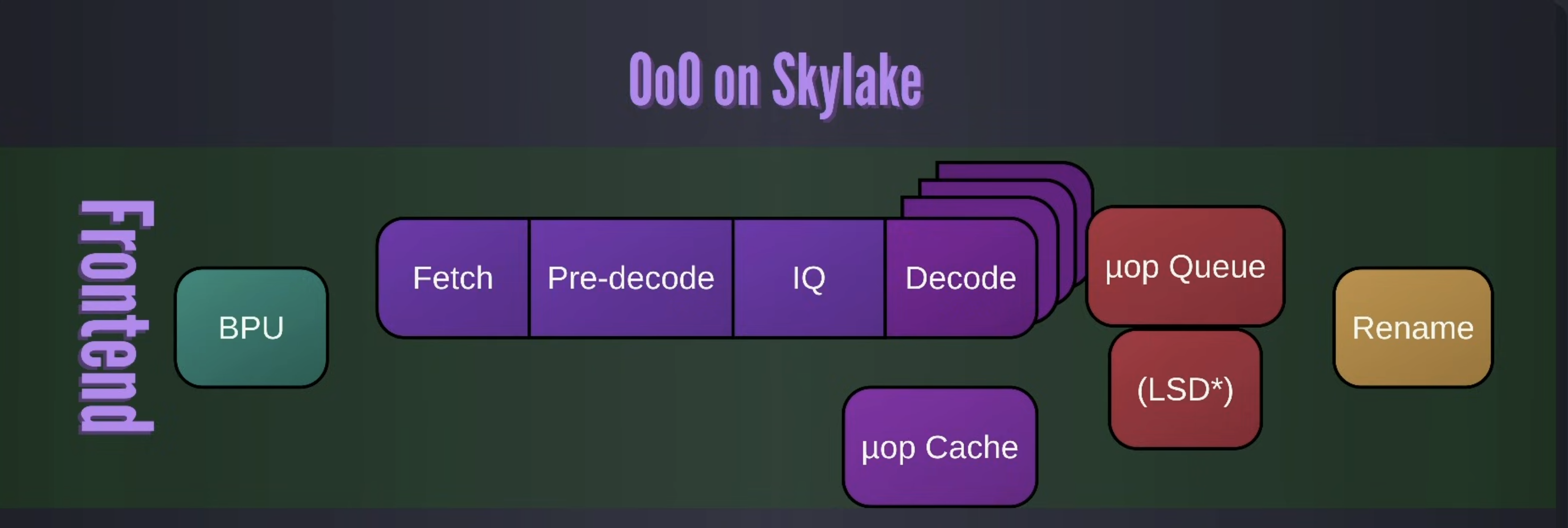
-
Predecoder can do uOp fusion
-
Decoder “steering” can happen here, we need a decoder because we need to convert from crazy x86 instructions into uOps
-
Parallelism

-
-
backend
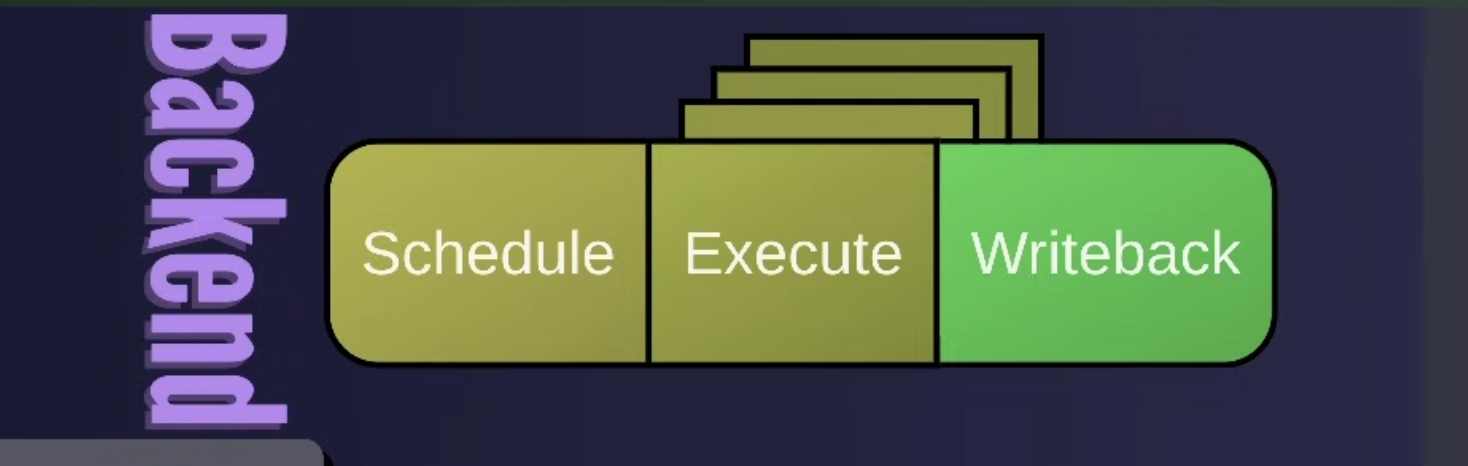
- retire and post retire
